Bush fire risk in the Lower Hunter
Fire agencies, land managers and other stakeholders have been working to identify ways of reducing the impact of fires on our area – protecting lives, homes, businesses, agriculture, the environment and other assets that are important to the Lower Hunter.
The local Bush Fire Management Committee has developed a draft Bush Fire Risk Management Plan, which identifies the risks and the plans to protect them.
The plan identifies the risk to communities and the assets we all value. Using feedback from fire agencies, land managers and other stakeholders, the plan identifies ways of reducing the impact of fires across our area.
By planning together, we will help shape the Bush Fire Risk Management Plan for our area for the next five years.
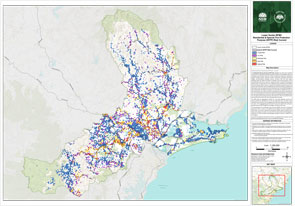
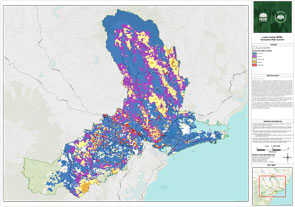
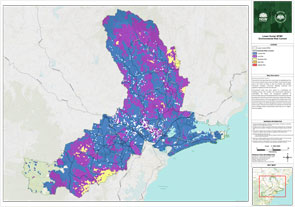
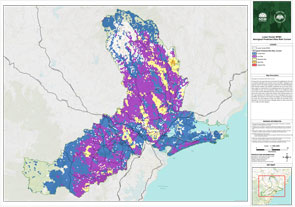
How the Lower Hunter Bush Fire Risk Management Committee have assessed the risk
Fire is a part of living in the Lower Hunter. It has been a part of this landscape for millions of years.
As our population and region changes, the risk of fires impacting on our community has changed.
To understand the bush fire risk in the Lower Hunter, and help inform the best ways of managing and reducing the risk, we’ve looked at what’s important to local communities – including where people live, as well as environmental, economic and cultural assets.
We look at the assets across the landscape, and using computer modelling, we have tested scenarios for possible fire conditions to understand the impact on the community.
Managing the risk in the Lower Hunter
We have considered the risk to people and assets across the area to determine the most appropriate and effective way of managing that risk.
Some areas of the Lower Hunter were impacted by the 2019/20 bush fire season, and these areas may have a reduced potential for fires spreading until vegetation fully recovers.
There are some measures which apply broadly – such as vegetation management, development controls, bush fire education, and fire suppression activities. These activities reduce the bush fire risk to assets and communities throughout the area.
Where an unacceptable risk exists for a particular area or assets, additional targeted treatment strategies are planned during the next five-year period. These treatment options include:
- Fuel management – the reduction or modification of bush fire fuel with the intent of slowing the spread of bush fire and aiding firefighting operations. This may be identified as;
- Asset protection zones – these are typically close to homes, and provide a separation from the bushland to reduce the impact of fires, and give firefighters a safe place to work if protecting homes in a fire;
- Ignition management zones – areas in the landscape maintained at a reduced fuel level to minimise the propagation of ignitions and limit the rapid escalation of fires;
- Strategic fire advantage zones – these are areas across the broad landscape which, when treated, can help slow the spread of a fire across the landscape;
- Firebreaks – areas designed and managed to provide fuel reduced areas from which a fire can be suppressed.
- Ignition prevention – activities to prevent or reduce bush fire ignitions whether they be accidental or deliberate. This includes community preparedness programs, fuel management and specific actions in the Ignition Prevention Plan.
- Community preparedness – activities such as working with residents to improve their level of planning and preparation for a fire, to increase the survivability of their home and families in the event of a fire.
- Response – specific response requirements for a particular area or value in addition to standard procedures. This may include specific actions in the BFMC Plan of Operations or Fire Access and Fire Trail plan.
Lower Hunter Bush Fire Management Committee is made up of a range of stakeholders from the area including emergency services, land management agencies, local government and local Aboriginal land services, and local community groups. This ensures key community stakeholders have a say on bush fire management activities for the benefit of their communities.
Lower Hunter Bush Fire Management Committee is made up representatives from the following agencies and organisations:
- NSW Rural Fire Service
- NSW Department of Planning and Environment (Crown Lands)
- Department of Defence
- Energy Australia
- NSW Farmers' Association
- Fire and Rescue NSW
- NSW Forestry Corporation
- Cessnock City Council
- Dungog Shire Council
- Port Stephens Council
- Maitland City Council
- Local Aboriginal Land Councils
- Nature Conservation Council of NSW
- NSW National Parks and Wildlife Service
- NSW Police Force
- Transport for NSW
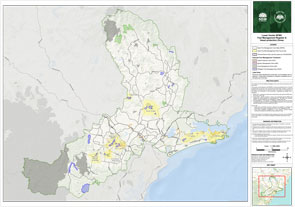
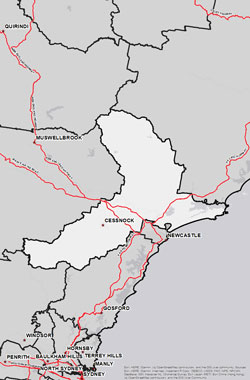
The Lower Hunter Bush Fire Management Committee (BFMC) area spans 557,113 ha. The area covers the Local Government Area/s (LGA) of Cessnock, Dungog, Maitland and Port Stephens and features National Parks covering an area of 111,068 ha and State Forests covering an area of 40,465 ha.
The Lower Hunter area has approximately 62.4% bushland and 31% grassland with the balance being the built environment or water bodies. A bush or grass fire can happen at any time of the year, but the risk is higher during the warmer months, when bush, grass or scrub is drier.
-
 According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) 2021 Census Community Profile there are 97,159 residential dwellings in the Lower Hunter BFMC area with an approximate population of 224,192.
According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) 2021 Census Community Profile there are 97,159 residential dwellings in the Lower Hunter BFMC area with an approximate population of 224,192. -
 According to the ABS data on the counts of Australian businesses, there were 14,195 businesses in the Lower Hunter BFMC. The top three industries in the BFMC are construction, professional, scientific and technical services and rental, hiring and real estate services, which make up approximately 41% of businesses in the Lower Hunter BFMC.
According to the ABS data on the counts of Australian businesses, there were 14,195 businesses in the Lower Hunter BFMC. The top three industries in the BFMC are construction, professional, scientific and technical services and rental, hiring and real estate services, which make up approximately 41% of businesses in the Lower Hunter BFMC. -
 The last major bush fires happened in the 2019/2020 Bush Fire Season – with 69,751 hectares burned.
The last major bush fires happened in the 2019/2020 Bush Fire Season – with 69,751 hectares burned. -
 There are multiple valuable community assets across the area along with a number of culturally significant sites and environmentally important sites.
There are multiple valuable community assets across the area along with a number of culturally significant sites and environmentally important sites.